What is being done about the Gulf of Mexico Dead Zone?
The EPA has committed to reducing the size of the Gulf dead zone and ideally, eliminating it altogether. Other organizations such as the Interagency Mississippi River and the Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Task Force are working to fight Gulf hypoxia as well.
How big is the ‘Dead Zone’ in the golf course?
Last year, the dead zone in the golf was about 6,300 square miles – “equivalent to more than four million acres of habitat potentially unavailable to fish and bottom species,” the Environmental Protection Agency said.
What is the Dead Zone and what causes it?
What Causes the Dead Zone? Heavy rains and melting snows washed massive amounts of nutrients—particularly nitrogen and phosphorus—from lawns, sewage treatment plants, farm land and other sources along the Mississippi River into the Gulf of Mexico.
How does the Dead Zone affect the fishing industry?
Because fish and other commercial species usually move out to sea in order to avoid the dead zone, fishermen are forced to travel farther from land—and spend more time and money—to make their catches, adding stress to an industry already hurt by hurricanes and the oil spill.
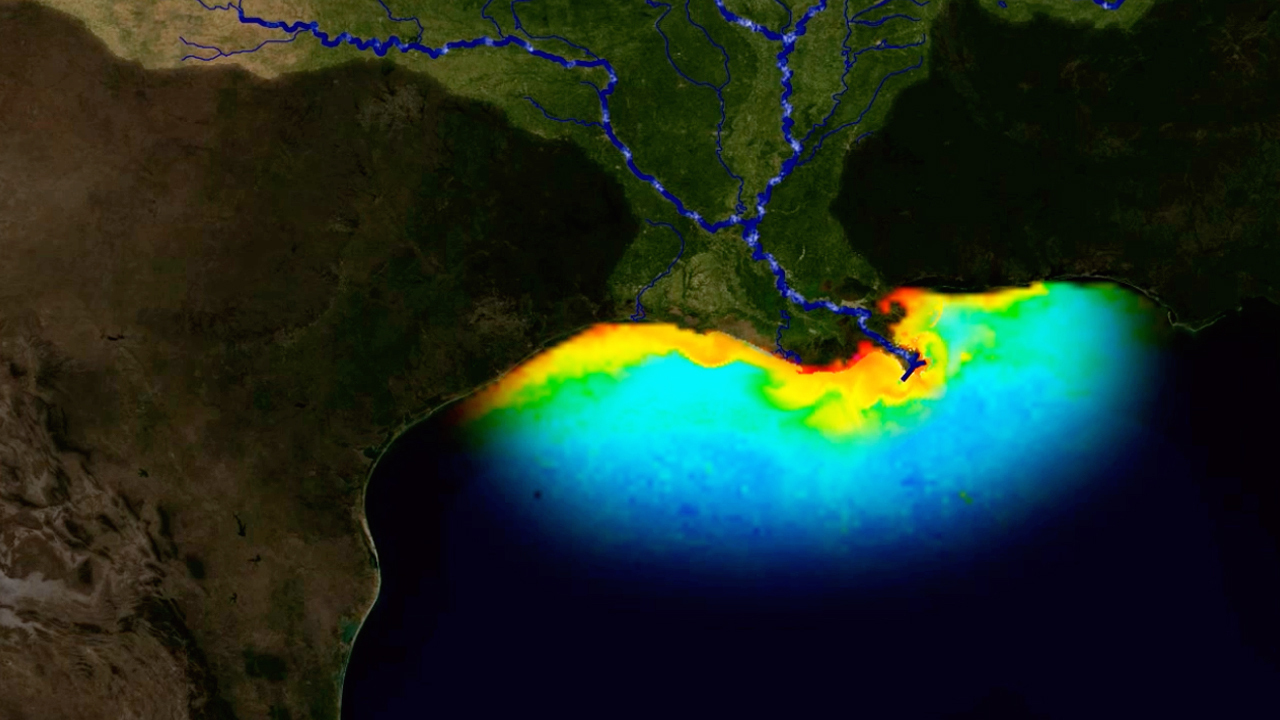
How are dead zones created?
Dead zones occur because of a process called eutrophication, which happens when a body of water gets too many nutrients, such as phosphorus and nitrogen. At normal levels, these nutrients feed the growth of an organism called cyanobacteria, or blue-green algae.
How are coastal dead zones created?
Hypoxic zones can occur naturally, but scientists are concerned about the areas created or enhanced by human activity. There are many physical, chemical, and biological factors that combine to create dead zones, but nutrient pollution is the primary cause of those zones created by humans.
Who is responsible for the dead zone in the Gulf of Mexico?
The primary culprit responsible for the growing size of the dead zone is an increasing supply of nitrogen dumped into the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River.
What is an ocean dead zone and how are they created?
A dead zone is an area of an ocean (or lake) that has too little oxygen to support marine life; it is hypoxic. This is a natural phenomenon that has been increasing in shallow coastal and estuarine areas as a result of human activities.
When did the Gulf of Mexico dead zone start?
1985Since records began in 1985, the largest hypoxic zone measured was 8,776 square miles in 2017.
When was the Gulf of Mexico dead zone discovered?
Scientists have determined this year's Gulf of Mexico “dead zone,” an area of low oxygen that can kill fish and marine life, is 8,776 square miles, an area about the size of New Jersey. It is the largest measured since dead zone mapping began there in 1985.
Where does the dead zone begin to form?
Dead zones begin to form when excess nutrients, primarily nitrogen and phosphorus, enter coastal waters and help fertilize blooms of algae. Major nutrient sources include fertilizers, wastewater, and the burning of fossil fuels.
Can you swim in dead zones?
In addition, the algal blooms that fuel dead zones can be detrimental to tourism and recreation because they can make water unsafe for swimming, release unpleasant odors, and cause fish kills that can wash hundreds of dead fish onto beaches.
What causes the dead zone in the Gulf of Mexico quizlet?
what causes a dead zone? Aquatic and marine dead zones can be caused by an increase in chemical nutrients (particularly nitrogen and phosphorus) in the water, known as eutrophication.
How deep is the dead zone?
At 3040 meters depth, the world completely cut off and all terrain would cease. It is unknown why this terrain was removed.
Can dead zones be fixed?
The good news is that a mix of forest and riparian habitat restoration and agricultural practices can help prevent future dead zones by stopping fertilizer from reaching the Gulf.
Are dead zones permanent?
Some are permanent. Some are natural. Some are made worse by human activity. Dead zones are areas within water bodies, usually in deep water near sediments, where there is insufficient oxygen to support life.
Why do dead plants fall into the Gulf?
As dead plant material falls from the surface through the water column deeper into the Gulf, bacteria consume it using oxygen. This lack of oxygen creates the Dead Zone in bottom waters on the Texas-Louisiana shelf throughout warm summer months. This occurs when there are fewer storms and strong winds to mix the warm, ...
How does the Environmental Defense Fund help farmers?
The Environmental Defense Fund is working with farmers to adopt practices that reduce fertilizer runoff, including partnering with the National Corn Growers Association to improve environmental outcomes while optimizing productivity and profitability . EDF scientists discovered that – with a combination of efficient fertilizer practices, cover crops and restoring wetlands and other natural infrastructure across the Corn Belt to trap and treat nitrogen lost from farms – we can reach the Environmental Protection Agency’s goal of shrinking the Gulf of Mexico’s dead zone to a safe level.
What can filter nutrients in the river water before it reaches the Gulf?
Broad floodplains filled with wetlands can filter nutrients in the river water before it reaches the Gulf. The river that was cut off from its floodplain by levees for flood control and channels for navigation can be reconnected via controlled diversions of water and sediment.
How does EDF help farmers?
These findings, along with parallel research highlighting the primary reasons for nitrogen losses in the Corn Belt, are helping inform policy and target agricultural funding where it is needed most. EDF has also: 1 Worked with farmers and their advisors to establish farmer networks that conduct real-world testing of fertilizer applications on farms. 2 Helped farmers share the results to determine best practices for delivering the highest yield with the greatest conservation benefits. 3 Helped reduce fertilizer loss by an average of 25% on 750,000 acres across the U.S. while maintaining or increasing crop yields.
What is the goal of the EDF?
EDF scientists discovered that – with a combination of efficient fertilizer practices, cover crops and restoring wetlands and other natural infrastructure across the Corn Belt to trap and treat nitrogen lost from farms – we can reach the Environmental Protection Agency’s goal of shrinking the Gulf of Mexico’s dead zone to a safe level.
Where are dead zones found?
Dead zones can be found worldwide (link to NASA dead zone page). The Gulf of Mexico dead zone is one of the largest in the world. Marine dead zones can be found in the Baltic Sea, Black Sea, off the coast of Oregon, and in the Chesapeake Bay. Dead zones may also be found in lakes, such as Lake Erie. Back to Top.
How to reduce dead zone?
The key to minimizing the Gulf dead zone is to address it at the source. Solutions include: 1 Using fewer fertilizers and adjusting the timing of fertilizer applications to limit runoff of excess nutrients from farmland 2 Control of animal wastes so that they are not allowed to enter into waterways 3 Monitoring of septic systems and sewage treatment facilities to reduce discharge of nutrients to surface water and groundwater 4 Careful industrial practices such as limiting the discharge of nutrients, organic matter, and chemicals from manufacturing facilities
What causes the dead zone in the Mississippi River?
The dead zone is caused by nutrient enrichment from the Mississippi River, particularly nitrogen and phosphorous. Watersheds within the Mississippi River Basin drain much of the United States, from Montana to Pennsylvania and extending southward along the Mississippi River.
What is the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico is a major source area for the seafood industry. The Gulf supplies 72% of U.S. harvested shrimp, 66% of harvested oysters, and 16% of commercial fish (Potash and Phosphate Institutes of the U.S. and Canada, 1999).
What happens if the hypoxic zone continues?
Consequently, if the hypoxic zone continues or worsens, fishermen and coastal state economies will be greatly impacted. Click to enlarge. When production increases in an ecosystem, organic matter, such as algal cells and fecal pellets, increases.
What causes dead zones in the Gulf of Mexico?
The dead zone in the Gulf is caused by a chain reaction of events, but that chain begins with humans. When farms around the Mississippi river or its tributaries get rain, the fertilizer in the soil can make it into the river itself. And once it's in the Mississippi, it's only a matter of time before it makes its way to the Gulf of Mexico.
When did scientists know about the Gulf Dead Zone?
History of the Gulf Dead Zone: Study. By the 1970s, scientists knew something was going on in the Gulf. The size of the dead zones reported by fishermen seemed, at least anecdotally, to be growing. By 1985, researchers were actively tracking the size and timing of the Gulf dead zone every year. Wikipedia.
What happens when algae dies in the Gulf of Mexico?
However, when these algae begin to die, the dead zone begins to take shape.
How big is the Gulf Dead Zone?
In 2019, scientists recorded the size of the Gulf Dead zone at just under 7000 square miles--6952, to be exact. That's just smaller than the state of New Jersey. Facebook.
What is a dead zone?
First things first--what even is a "dead zone"? It's the popular term for what scientists call "hypoxia"--or areas of low oxygen in large bodies of water. Some of these dead zones have occurred naturally throughout history, but something else is going on in the Gulf of Mexico. Facebook.
What happens when algae dies?
As the algae die off, microscopic bacteria begin the decomposition process. Their presence reduces the oxygen levels in the surrounding waters, sometimes to a point where its detrimental to other marine life.
When did shrimp trawlers start reporting areas off the coast that had unusually low numbers of live shrimp for
Even before scientists started studying the dead zone closely, other people had begun to suspect that something was up in the Gulf of Mexico. In the 1950s , shrimp trawlers began reporting areas off the coast that had unusually low numbers of live shrimp for catching.
How big was the dead zone in the Gulf of Mexico in 1988?
In 1988 the Gulf of Mexico's dead zone was only 15 square miles (a record low), and in 2002 it reached 8,400 square miles (record high) in size.
When did the dead zone in the Gulf of Mexico become smaller?
In 1988 the Gulf of Mexico's dead zone was only 15 square miles (a record ...
What is the dead zone in the Gulf of Mexico?
The Gulf of Mexico dead zone is an area in the Gulf of Mexico where excessive pollution has resulted in an inadequate level of oxygen needed to support life. Dead zones occur where aquatic life is more concentrated, in areas with coastlines inhabited by humans. Despite the ocean's middle portions being sparsely populated by aquatic life, these regions are not considered dead zones. There are approximately 405 known dead zones in the world's oceans today, with the Gulf of Mexico's dead zone being the largest recurring hypoxic zone on earth. Hypoxic means low-oxygen, and this dead zone in particular occurs each summer for several weeks.
Where are dead zones?
Some of the more well-known dead zones in the world include the Gulf of Mexico dead zone, the Baltic Sea dead zone, the Black Sea dead zone, in Lake Erie (one of the freshwater lakes of the Great Lakes), off the coast or Oregon, and in Chesapeake Bay. Dead zones can be reversed with proper environmental efforts.
When did the dead zone disappear?
The dead zone in the Black Sea disappeared in 1991 when fertilizer use diminished greatly because of its high cost. This dead zone reversal was not intentional but it has been helpful in providing influence in reversing other dead zones.
How many dead zones are there in the ocean?
There are approximately 405 known dead zones in the world's oceans today, with the Gulf of Mexico's dead zone being the largest recurring hypoxic zone on earth. Hypoxic means low-oxygen, and this dead zone in particular occurs each summer for several weeks. The first time the Gulf of Mexico's dead zone was reported was in 1950.
How big is the dead zone in 2015?
The 2015 “Dead Zone” measured 16,760 square kilometers (6,474 square miles). This size is larger than the predicted range made in June. Researchers suggest that heavy rains in June and high river discharges in July may provide an explanation for the larger zone measurement.
How big is the Gulf of Mexico hypoxic zone?
The 2020 Gulf of Mexico hypoxic zone or "dead zone" measured 2,116 square miles and was the 3rd smallest in the 34-year record of surveys. The 5-year average is now down to 5,408 square miles. The earlier forecast for the dead zone was higher at 6,700 square miles. A major factor for the smaller measured size was due to extensive mixing caused by hurricane Hanna, which passed through the Gulf right ahead of the survey cruise. For more information, see the Lousiana Universities Marine Consortium (LUMCON) Exit and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) Exit press releases. Map of measured Gulf hypoxia zone, July-August 2020. (LUMCON/NOAA)
What is the hypoxia zone in the Gulf of Mexico?
NOAA and the United States Geological Survey (USGS) released their summer hypoxia zone size in the Northern Gulf of Mexico on June 3, 2020. Read the full press release here. Exit Scientists are forecasting this summer’s Gulf of Mexico hypoxic area or “dead zone” – an area of low to no oxygen that can kill fish and other marine life – to be approximately 6,700 square miles, larger than the long-term average measured size of 5,387 square miles but substantially less than the record of 8,776 square miles set in 2017. The annual prediction is based on U.S. Geological Survey river-flow and nutrient data.
Why was the hypoxic zone not measured in 2016?
Due to mechanical problems with the NOAA ship designated for the measurement cruise , the hypoxic zone was not measured in 2016. Read the full press release for more information Exit .
Where is the hypoxic zone?
The hypoxic zone in the northern Gulf of Mexico is an area along the Louisiana-Texas coast, where water near the bottom of the Gulf contains less than two parts per million of dissolved oxygen, causing a condition referred to as hypoxia.
How big is the dead zone in Mississippi?
The 2017 “Dead Zone” measured 22,720 square kilometers (8,776 square miles). This size is close to the forecast made in June. Researchers suggest that the Mississippi River May discharge, which was well above average, provides an explanation for most of the large zone measurement.
Why is the size of the hypoxic zone important?
The size of the zone is an important indicator of how much progress is being made to reduce nutrient inputs into the Gulf of Mexico.
Where is the dead zone?
1). The zone forms west of the Mississippi Delta over the continental shelf off Louisiana and sometimes extends off Texas. The oxygen depletion begins in late spring, increases in summer, and ends in the fall.
What is the dead zone in Louisiana?
Rabalais (CENR, 2000). The hypoxic szone, also called the dead zone, varies in size and shape and duration; hypoxia is defined as oxygen concentrations in subsurface water of less than 2 milligrams per liter.