Common Causes
Mayo Clinic Q and A: Golfer’s elbow and when to see your doctor. The medical term for golfer’s elbow is medial epicondylitis. It happens when muscles and tendons that control flexing of your wrist and fingers are damaged, often by too much stress or repeated stress due to forceful wrist and finger motions.
Related Conditions
Golfer's elbow. Overview. Golfer's elbow is a condition that causes pain where the tendons of your forearm muscles attach to the bony bump on the inside of your elbow. The pain might spread into your forearm and wrist. Golfer's elbow is similar to tennis elbow, which occurs on the outside of the elbow. It's not limited to golfers.
When to see a doctor for golfer’s elbow?
Golfer's elbow is a condition that causes pain where the tendons of your forearm muscles attach to the bony bump on the inside of your elbow.
What does it mean when you have elbow pain in golf?
To evaluate pain and stiffness, the doctor might apply pressure to the affected area or ask you to move your elbow, wrist and fingers in various ways. An X-ray can help the doctor rule out other causes of elbow pain, such as a fracture or arthritis.
What is golfer's elbow and how is it treated?
How do you test for elbow pain?

Do you need to go to the doctor for golfers elbow?
You should seek immediate medical attention for golfer's elbow and tennis elbow if the area of pain is also inflamed, and the discomfort is accompanied by a fever. You should also obtain prompt medical care if you are unable to bend your elbow, or are experiencing any numbness or weakness in your hand .
Does golfers elbow show on xray?
Radiographs. X-rays are usually negative in patients with golfer's elbow. Office x-rays are commonly obtained to rule out other pathology, such as fracture, dislocation, or bone lesion. Occasionally, calcifications can be seen adjacent to the medial epicondyle in chronic cases.
Does golfers elbow show up on ultrasound?
Golfer's elbow is common in manual workers and those that play racquet sports and lift heavy weights. It does not only occur in those that play golf! It is relatively easy to diagnose and a diagnostic ultrasound can confirm the severity of your condition and whether or not there is a tear in the tendon.
Can an MRI show golfers elbow?
It's not as clear and detailed as an MRI but in areas where the tendon or other tissue is close to the surface of the body (like the elbow) it can produce a very reliable image. When this technology best comes into play for Tennis and Golfer's Elbow is as a screening tool.
What is the fastest way to fix golfers elbow?
Try the following:Rest. Put your golf game or other repetitive activities on hold until the pain is gone. ... Ice the affected area. Apply ice packs to your elbow for 15 to 20 minutes at a time, three to four times a day for several days. ... Use a brace. ... Stretch and strengthen the affected area.
Will a cortisone shot help golfers elbow?
By strengthening the tendons and muscles involved with golfer's elbow, the patient can help keep the problem from returning. Cortisone injections. If other conservative treatments for golfer's elbow fail, a cortisone (steroid) injection may be considered.
How painful is golfer's elbow?
Usually felt on the inner side of your elbow, the pain sometimes extends along the inner side of your forearm. Pain typically worsens with certain movements. Stiffness. Your elbow may feel stiff, and making a fist might hurt.
Does a brace help golfers elbow?
If you have medial epicondylitis, better known as golfer's elbow, wearing a special brace around your forearm can help with symptoms.
How long does it take golfers elbow to heal?
Fortunately, most people recover from golfer's elbow without surgery and after resting their arm for about six weeks. It's also good news there are simple steps you can take every day that can help your tendons heal.
How do you sleep with golfers elbow?
Try sleeping on your back with your affected arm straight along your side. Use positioning pillows or folded blankets to help keep your body and arm in position. Avoid applying pressure to the affected arm. This will help reduce inflammation and swelling in the elbow.
What happens if golfers elbow goes untreated?
When you repeatedly use your wrist and arm to bend, grasp or twist things, your tendons develop tiny tears that can cause wrist, elbow and forearm pain. Left untreated, golfer's elbow could cause permanent damage like limiting your elbow's range of motion, causing chronic pain and weakening your grip.
Where is golfer's elbow pain?
Medial epicondylitis is also known as golfer's elbow, baseball elbow, suitcase elbow, or forehand tennis elbow. It's characterized by pain from the elbow to the wrist on the inside (medial side) of the elbow. The pain is caused by damage to the tendons that bend the wrist toward the palm.
How long does it take golfers elbow to heal?
Give Your Self Time The good news is that golfer's elbow often heals on its own. Since it is a repetitive strain injury, the main factor affecting your healing is time away from the repetitive motion that caused the problem. How much time? Six weeks or so seems to be adequate.
How do you XRAY an elbow joint?
Position of part Place the arm on the table with the elbow straight and the palm of hand straight up. Ideally, the upper arm, elbow, and forearm are all resting on the table. Extend the elbow and keep the hand supinated, palm up. Central ray Perpendicular to the image receptor at the joint of the elbow.
How to prevent golfer's elbow?
You can take steps to prevent golfer's elbow: Strengthen your forearm muscles. Use light weights or squeeze a tennis ball. Even simple exercises can help your muscles absorb the energy of sudden physical stress. Stretch before your activity. Walk or jog for a few minutes to warm up your muscles.
Where does golfer's elbow pain occur?
The pain of golfer's elbow occurs primarily where the tendons of the forearm muscles attach to the bony bump on the inside of the elbow ( medial epicondyle). By contrast, the pain of tennis elbow usually occurs at the bony bump on the outside of the elbow (lateral epicondyle).
What is golfer elbow?
Golfer's elbow is a condition that causes pain where the tendons of your forearm muscles attach to the bony bump on the inside of your elbow. The pain might spread into your forearm and wrist.
What is the cause of golfer's elbow?
Golfer's elbow, also known as medial epicondylitis, is caused by damage to the muscles and tendons that control your wrist and fingers. The damage is typically related to excess or repeated stress — especially forceful wrist and finger motions.
What can overload the elbow muscles?
Weight training. Lifting weights using improper technique, such as curling the wrists during a biceps exercise , can overload the elbow muscles and tendons.
What does it mean when your elbow hurts?
Pain typically worsens with certain movements. Stiffness. Your elbow may feel stiff, and making a fist might hurt. Weakness. You may have weakness in your hands and wrists.
What causes elbow pain in golf?
Improper lifting, throwing or hitting, as well as too little warmup or poor conditioning, also can contribute to golfer's elbow. Besides golf, many activities and occupations can lead to golfer's elbow, including: Racket sports.
What are the risk factors for golfer elbow?
Other possible risk factors for golfer’s elbow include: Carrying a heavy suitcase for extended periods. Chopping wood with an ax. Using a computer regularly. Frequent use of other hand tools (screwdrivers, raking, etc.) Sports that involve a lot of throwing or swinging (baseball, tennis, javelin, etc.)
Why is it called golfer's elbow?
It is referred to as golfer’s elbow because the tendon is typically stressed while making a golf swing with a non-overlapping grip. It is also known as baseball elbow, suitcase elbow, or forehand tennis elbow. Therefore, you can get it even if you’ve never picked up a golf club.
What does it mean when your elbow hurts?
Forearm, hand, and wrist pain. Numbness, tingling, and stiffness. Difficulty making a fist. Pain when shaking someone’s hand. Difficulty moving the elbow. Swelling and tenderness.
Where is the pain in the elbow?
The pain and inflammation are located on the inside of the elbow—rather than the outside—where the forearm muscles connect to the bone. When the tendon is overused due to repeated hand, arm, and wrist motions, the site becomes aggravated and causes pain. The condition affects men more than women by a ratio of 2:1.
Can golfer's elbow heal on its own?
Golfer’s elbow, just like many overuse injuries, can affect anyone and may even heal on its own. However, you should follow your doctor’s instructions, which will likely include rest, to avoid this condition getting worse.
Can you get elbow pain if you have never picked up a golf club?
Therefore, you can get it even if you’ve never picked up a golf club. Musculoskeletal pain is the No. 1 reason people visit their doctors each year. It is very common to be referred to an orthopedic doctor for further evaluation on elbow pain regardless if you play sports or not.
Medical History
To begin with, your doctor will gather a medical history about you and your current condition and symptoms. They will inquire about the intensity of your present pain, the duration of your symptoms and the limitations you are experiencing (i.e. does it hurt when you move your wrist). The diagnosis will be based on:
Physical Examination
A physical examination will be performed to determine if you have any signs of tennis elbow, golfer's elbow or other elbow injuries. During your physical exam, your doctor will visually assess your elbow by asking you to extend and flex your elbow, wrist, and fingers.
Struggling To Rid Yourself of Tennis Elbow?
The good news is that most cases of tennis elbow will heal with simple home conservative treatments and surgery is often not needed! It's generally understood by doctors and surgeons, that surgery will introduce more scar tissue into the elbow.
How to prevent golfer's elbow?
First, stretching before you engage in the exercise activity that has resulted in your pain can be beneficial.
Where is the pain in golfer's elbow?
If you are dealing with golfer’s elbow, the pain that you experience will be located where the forearm muscles are joined with the inside of your elbow. The pain will likely occur at the inner side of your elbow, although this discomfort can also advance into the inner portion of your forearm or your wrist. Other symptoms for this condition include stiffness, along with weakness, numbness, and tingling. Usually, the issue becomes worse as time progresses unless steps are taken to treat the condition.
What is the pain in the elbow?
This form of elbow tendonitis involves the tendons that attach your forearm muscles to the outside of your elbow. The pain can also proceed into the wrist, or the forearm. This discomfort can intensify whenever you are attempting to grip an object, make a fist, lift an item, open a door, or shake someone’s hand.
How old do you have to be to get tennis elbow?
The chances of tennis elbow occurring rise for anyone who is at least 30 years of age. The risks of experiencing this issue also rise in a similar fashion to the factors that increase your chances of being confronted with golfer’s elbow, which is participation in sports or recreational activities that make it necessary to make a repetitive movement. This also remains the case for any professionals who must engage in repeated motion each day in order to perform their jobs.
How to strengthen elbows?
This includes using a lighter set of golf clubs or a tennis racquet that has the correct size for your grip. You can also take steps to bolster the strength of your elbow by (ironically) squeezing a tennis ball.
Can you get golfer's elbow at 40?
Sports-related activities that involve the use of a racket, or require a frequent throwing motion, can lead you toward the path of having this condition. Your chances of experiencing golfer’s elbow will also increase once you have reached age 40. This is also the case if you are obese, or if you are a smoker.
Is tennis elbow the same as golfer's elbow?
But even though golfer’s elbow and tennis elbow are comparable, there is a distinct difference between these two issues.
How should patients with golfer's elbow be managed?
A prescription for physical therapy should include directions for stretching and eccentric training of the flexor tendons around the elbow. Eccentric training is when the muscle is contracting as it is being elongated (i.e. a “negative” repetition). Prescribers should also write “modalities prn” so that the therapist can use ultrasound and iontophoresis with a steroid cream at their discretion. Duration of therapy is 6 weeks to start.
What causes a skeletally immature athlete to have pain in their elbow?
Physeal (growth plate) injury (little leaguer's elbow) Common cause of medial elbow pain in skeletally immature throwers. Referral to a pediatric orthopaedic surgeon should be considered when treating a skeletally immature patient with medial elbow pain since physeal injuries and fractures are more common than golfer’s elbow in this population.
What nerve causes anteromedial elbow pain?
Cubital tunnel syndrome can mimic golfer’s elbow. Median nerve entrapment in the pronator is a rare cause of anteromedial elbow pain.
What does it mean when your elbow is in extension?
Tenderness to palpation over the medial epicondyle is the hallmark of the diagnosis. With the elbow in extension, patients will have pain with passive wrist extension and resisted wrist flexion. They may also have pain with resisted forearm pronation.
What nerve is entrapped at the elbow?
Entrapment of the ulnar nerve at the elbow. Care must be taken to assess the motor and sensation of the ulnar nerve, and to determine if the patient has a subluxing ulnar nerve. If suspected, EMG’s should be performed.
Where is the injection placed for ulnar nerve?
Injection is placed at the site of maximal tenderness taking care to avoid the ulnar nerve if is subluxed anterior to the medial epicondyle. The injection should go around the tendon, not into the tendon. This is accomplished by inserting the needle into the tendon, then gently pushing down on the plunger while pulling the needle back. As soon as minimal resistance is felt on the plunger, then the needle is adjacent to the tendon and the contents of the injection can be delivered.
Can an MRI be done on elbow?
Usually not needed in the early stages. If symptoms persist with non-operative management, an MRI is obtained to assess the extent of elbow involvement, and to determine if the tendon is torn from the bone. MRI can also rule out concomitant pathology.
How to diagnose golfer's elbow?
Diagnosing Golfer's Elbow. To diagnose golfer's elbow, an orthopaedic specialist evaluates your symptoms, examines your elbow and forearm, and discusses any sports or daily activities that may have led to the condition. You will likely require further imaging tests to assess the damage to the tissues in your elbow and forearm, such as: CT scan.
What is the treatment for golfer's elbow?
Noninvasive therapy for golfer's elbow includes: Extracorporeal shock wave therapy, an ultrasound-guided technique that sends energy waves to damaged soft tissues in the elbow. If your symptoms do not improve within several months, you may have torn tendons and/or ligaments that require surgery.
What causes pain in the inside of the arm and elbow?
Often mistaken for tennis elbow (pain and inflammation on the outside of the elbow), golfer's elbow causes pain and inflammation on the inside of the arm and elbow. Repetitive motions — such as gripping, flexing and swinging — cause golfer's elbow. If you experience the following symptoms, see a Penn orthopaedic specialist to be evaluated ...
What is golfer's elbow?
Golfer's elbow (medial epicondylitis) is an inflammation of the tendons that attach the muscles of the forearm to the bone on the inside of the elbow. It is a form of tendinitis of the elbow. Often mistaken for tennis elbow (pain and inflammation on the outside of the elbow), golfer's elbow causes pain ...
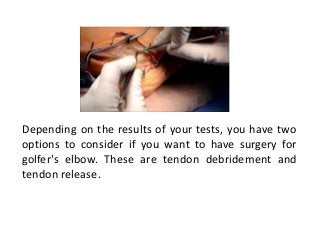
How to heal after golfer's elbow surgery?
After golfer's elbow surgery, rest is very important for healing. After surgery, your arm and elbow will be immobilized in a sling or splint, and you should keep it elevated to help limit inflammation. Individuals who experience less pain during recovery tend to have better results. Our advanced pain management program effectively treats pain with less dependence on narcotics. Your doctor will want you to begin a pain management program and physical therapy as soon as possible after surgery to maintain and build tendon and ligament strength and to help regain mobility. Your doctor will determine when you should begin your rehabilitation program.
What does it mean when your elbow hurts?
Elbow pain and tenderness on the inside of your elbow. Elbow weakness . Numbness, burning and tingling in the fingers. Pain and/ or burning that radiates down the inner side of the forearm.
What is open tendon repair?
Open Tendon Repair. If a tendon tear is large and there is a lot of soft tissue damage in the elbow and forearm, your surgeon may choose to perform open tendon repair. Open tendon repair is used for complex injuries that require multiple procedures to be performed at once.
