| Falling object | Mass | Terminal velocity |
|---|---|---|
| Baseball (3.66cm radius) | 145 gm | 74 mi/hr |
| Golf ball (2.1 cm radius) | 46 gm | 72 mi/hr |
| Hail stone (0.5 cm radius) | .48 gm | 31 mi/hr |
| Raindrop (0.2 cm radius) | .034 gm | 20 mi/hr |
What is the terminal velocity of a golf ball?
The terminal velocity of a golf ball, using either the calculators or the spreadsheet, is about 33.8 m/s, while that of the tennis ball is about 21.5 m/s. Clearly the golf ball falls "faster" than the tennis ball.
What is terminal velocity?
What is Terminal Velocity? What is Terminal Velocity? Terminal velocity is defined as the maximum velocity an object can achieve when falling through a fluid, such as air or water. That happens when the gravitational force working on the object in downward direction equals the sum of upward forces (drag and buoyancy) impeding it's fall.
How do you find the terminal velocity of a sphere?
w = F t + F v … …. ( i) After this net force on the sphere is zero and it moves downwards with a constant velocity called terminal velocity ( v t). Substituting proper values in Eq. ( i) we have, η = coefficient of viscosity of fluid. So the terminal velocity ( v t) is directly proportional to the square of the radius of the sphere.
How can you tell the difference between tennis ball and golf ball?
You might be able to detect that difference if your observation skills are very good. The terminal velocity of a golf ball, using either the calculators or the spreadsheet, is about 33.8 m/s, while that of the tennis ball is about 21.5 m/s. Clearly the golf ball falls "faster" than the tennis ball.

How do you find the terminal velocity of a ball?
How do I find terminal velocity? To calculate terminal velocity: Multiply the mass of the object by the gravitational acceleration. Divide the resultant by the product of drag coefficient and projected area.
What is the exit velocity of a golf ball?
51 feet per second, or approximately one-third of 1 mph. According to Thomas, the rule was adopted in 1942 to limit the distance the balls were traveling.
Can a ball reach terminal velocity?
The ball will slow down to terminal velocity. This is because the force of air drag increases with increasing speed. Terminal velocity is the speed where the force of air drag equals the force of gravity, so the total force is zero and the object travels at a constant speed.
Which falls faster a tennis ball or a golf ball?
The tennis ball and the golf ball hit the ground at the same time. The Earth's gravity is so strong that it pulls objects like these at the same speed. The feather falls more slowly than a golf ball.
What is the farthest a golf ball has ever been hit?
515 yardsThe world record recognized by Guinness World Records as the longest drive in a competition is 515 yards (471 m) by 64-year-old Mike Austin in 1974 at the US Senior National Open Qualifier with a 43.5" steel shafted persimmon wood driver.
What is the fastest a golf ball has ever hit?
The fastest golf drive is 349.38 km/h (217.1 mph) and was achieved by Ryan Winther (USA) at the Orange County National Driving Range in Orlando, Florida, USA, on 23 January 2013.
Can a mouse survive terminal velocity?
So the resistance to falling in the case of the small animal is relatively ten times greater than the driving force.” This is why the terminal velocity of a mouse is so much less than that of a horse. Thus, the mouse likely survives a high fall and a horse splats.
What is the terminal velocity of a human?
about 200 km/hIn a stable, belly to earth position, terminal velocity of the human body is about 200 km/h (about 120 mph). A stable, freefly, head down position has a terminal speed of around 240-290 km/h (around 150-180 mph).
What is the fastest terminal velocity?
134 km/hrThis is about the same as the terminal velocity achieved by a peregrine falcon diving for prey or for a bullet falling down after having been dropped or fired upward. The world record terminal velocity was set by Felix Baumgartner, who jumped from 39,000 meters and reached a terminal velocity of 134 km/hr (834 mph).
What falls faster a brick or a penny?
Answer 2: No, heavier objects fall as fast (or slow) as lighter objects, if we ignore the air friction. The air friction can make a difference, but in a rather complicated way. The gravitational acceleration for all objects is the same.
What falls faster feather or brick?
The bricks are more compact and dense and would fall faster than the pound of feathers. The pound of feathers would have so much more surface area and lower density that they would fall much slower than the bricks.
Will a penny and a bowling ball fall at the same rate?
Answer. If no air resistance is present, the rate of descent depends only on how far the object has fallen, no matter how heavy the object is. This means that two objects will reach the ground at the same time if they are dropped simultaneously from the same height.
What is terminal velocity?
Terminal velocity is defined as the highest velocity which can be attained by an object during its falling through the air. It happens when the sum...
Does terminal velocity exist in a vacuum?
In a vacuum, since there is no drag force, the terminal velocity does not exist.
What does Terminal Velocity depend on?
Terminal velocity is the point at which the drag force equals the force of gravity. Hence, terminal velocity will depend on the mass, cross-section...
Why a flat piece of paper will fall more slowly as compared to the same paper after it has been crum...
The paper weighs the same, but the air drag forces on the ball have decreased because its surface area has decreased. Due to this, the crumpled pap...
Give an application of the terminal velocity in our life?
Parachutes and hang gliders. As it is possible to increase or decrease the terminal velocity by making some changes in your weight or shape, or alt...
What is the terminal velocity equation?
The terminal velocity equation tells us that an object with a large cross-sectional area or a high drag coefficient falls slower than an object with a small area or low drag coefficient. A large flat plate falls slower than a small ball with the same weight.
Why is the drag coefficient higher?
For airflow near and faster than the speed of sound , there is a large increase in the drag coefficient because of the formation of shock waves on the object.
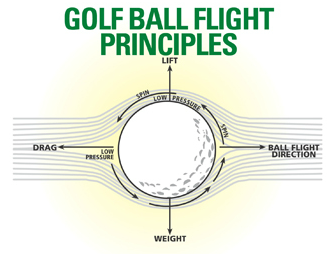
What is the net external force of weight and drag?
Weight and drag are forces which are vector quantities . The net external force F is then equal to the difference of the weight W and the drag D. F = W - D. The acceleration of a falling object then becomes: a = (W - D) / m. The magnitude of the drag is given by the drag equation.
How does drag increase with speed?
Drag increases with the square of the speed . So as an object falls, we quickly reach conditions where the drag becomes equal to the weight, if the weight is small. When drag is equal to weight, there is no net external force on the object and the vertical acceleration goes to zero.
What is the force that falls through the atmosphere?
An object which is falling through the atmosphere is subjected to two external forces. One force is the gravitational force, expressed as the weight of the object. The other force is the air resistance, or drag of the object. If the mass of an object remains constant, the motion of the object can be described by Newton's second law of motion, ...
Does Galileo's principle apply to vacuum?
But Galileo's principle only applies in a vacuum, where there is NO air resistance and drag is equal to zero.
Is the drag coefficient of a terminal velocity high?
If your drag coefficient includes compressibility effects, then your answer is correct. If your drag coefficient was determined at low speeds, and the terminal velocity is very high, you are getting the wrong answer because your drag coefficient does not include compressibility effects. The terminal velocity equation tells us ...
What is Terminal Velocity?
When the ball is thrown into the sea, It accelerates initially due to gravity. As the velocity increases, the retarding force also increases (by Stokes’s Law). Finally, the net force becomes zero when the viscous force plus buoyant force becomes equal to the force due to gravity, and so does the acceleration.
Terminal Velocity Formula (vt)
Consider a small sphere shown in Fig. (b) is falling from rest through a large column of viscous fluid. The forces acting on the sphere are:
Terminal Velocity Formula– Sample Problems
Q.1. Assume that a spherical body is flowing through the water. The velocity of the body at a particular instant is 2 m s – 1. What will be the drag force on the body due to the fluid? Assume that Stokes’s law is valid.
Summary
The property of a fluid by which an internal frictional force acts between its different layers which oppose their relative motion is called viscosity. The ratio of the shear stress to the time rate of shearing strain is known as the coefficient of viscosity ( η). The coefficient of viscosity ( η) falls when the temperature rises and vice versa.
FAQs on Terminal Velocity Formula
Q.1. What is terminal velocity? Ans: Terminal velocity is defined as the highest velocity which can be attained by an object during its falling through the air. It happens when the sum of the dragged force ( ( F d) and the buoyancy is equal to the downward force of gravity ( F g) acting on the body and the net force acting on the object is zero.
What is terminal velocity?
Terminal velocity, steady speed achieved by an object freely falling through a gas or liquid. A typical terminal velocity for a parachutist who delays opening the chute is about 150 miles (240 kilometres) per hour.
What is the force of air resistance at terminal velocity?
At terminal velocity, air resistance equals in magnitude the weight of the falling object. Because the two are oppositely directed forces, the total force on the object is zero, and the speed of the object has become constant.
How does air resistance affect the speed of an object?
The force of air resistance is approximately proportional to the speed of the falling object, so that air resistance increases for an object that is accelerating, having been dropped from rest until terminal velocity is reached. At terminal velocity, air resistance equals in magnitude the weight of the falling object.
What is terminal velocity?
Terminal velocity is the maximum velocity (speed) attainable by an object as it falls through a fluid ( air is the most common example). It occurs when the sum of the drag force ( Fd) and the buoyancy is equal to the downward force of gravity ( FG) acting on the object. Since the net force on the object is zero, the object has zero acceleration.
Which object has a lower terminal velocity?
An object with a large projected area relative to its mass, such as a parachute, has a lower terminal velocity than one with a small projected area relative to its mass, such as a dart. In general, for the same shape and material, the terminal velocity of an object increases with size.
What happens when the net force is zero?
Since the net force on the object is zero, the object has zero acceleration. In fluid dynamics, an object is moving at its terminal velocity if its speed is constant due to the restraining force exerted by the fluid through which it is moving.
What is the force of resistance when an object stops accelerating?
At some speed, the drag or force of resistance will equal the gravitational pull on the object (buoyancy is considered below). At this point the object stops accelerating and continues falling at a constant speed called the terminal velocity (also called settling velocity).
What is terminal velocity?
Terminal velocity is defined as the highest velocity that can be achieved by an object that is falling through a fluid, such as air or water. When terminal velocity is reached, the downward force of gravity is equal to the sum of the object's buoyancy and the drag force. An object at terminal velocity has zero net acceleration .
How are terminal velocity and free fall related?
Terminal velocity and free fall are two related concepts that tend to get confusing because they depend on whether or not a body is in empty space or in a fluid (e.g., an atmosphere or even water). Take a look at the definitions and equations of the terms, how they are related, and how fast a body falls in free fall or at terminal velocity ...
How fast does a person fall through the air?
In general, a person falling through the air on Earth reaches terminal velocity after about 12 seconds, which covers about 450 meters or 1500 feet. A skydiver in the belly-to-earth position reaches a terminal velocity of about 195 km/hr (54 m/s or 121 mph).
What is free fall in physics?
In classical mechanics, free fall describes the motion of a body when the only force acting upon it is gravity.
Is the direction of the gravitational field important?
The direction of the movement ( up, down, etc.) is unimportant. If the gravitational field is uniform, it acts equally on all parts of the body, making it "weightless" or experiencing "0 g". Although it might seem strange, an object can be in free fall even when moving upward or at the top of its motion.
How far can a 0.308 bullet be fired?
To complicate matters further, the US Army defines the maximum effective range of a 0.308 as 800 m. The US Marine Corps defines the effective range as 1000 m. The US Army also states that bullets are no longer effective once they become subsonic, which happens at around 1000 m with a 0.308.
What causes a bullet to drift?
Drift is caused by the rifling of the bullet. This is a result of the gyrostatic properties of the rifling-induced spin of a bullet. This effect gives bullets with a right-hand spin a drift to the right and left-hand spinning bullets a drift to the left.
How fast does a bullet penetrate skin?
Haag, 'the bullet velocity required for skin penetration is between 147 and 196 ft/sec which is within the velocity range of falling bullets .'.
What is the maximum range of a shotgun?
The formula most often quoted for maximum range of shot is known as Journee -s Formula, which states simply that the maximum range in yards is equal to 2200 times the diameter of the shot in inches .
How many yds does a 0.22 rifle have?
To compensate for the bullet drop due to gravity, the sights are raised to give the barrel sufficient elevation that the bullet will strike the target at a set distance. For handguns, this is generally 10 yd; for a 0.22" rifle, 25 yd and for full-bore rifles, generally 200 yd (Figure 3.2).
Why is maximum effective range so difficult to quantify?
The 'maximum effective range ' is probably even more difficult to quantify due to the number of variables which come into play, that is, bullet weight, bullet design, velocity, bullet diameter, bullet placement, weapon accuracy, and so on. Each and every situation must, therefore, be taken on its own merit.
What is the maximum effective range?
The US Military states ' the maximum effective range is the maximum range within which a weapon is effective against its intended target,' and calls for ' a delivery of between 35 and 270 ft/lbs to be effective'. A somewhat rather large spread of values.
What is terminal velocity?
Follow Us: The terminal velocity of a free-falling human depends on the mass and density of the person. In general, the heavier the body, the longer it can accelerate before drag holds it at a constant speed. For a typical human, terminal velocity ranges between ...
How fast can a skydiver go in bullet position?
A skydiver in the bullet position usually achieves this speed within six or seven seconds. After that, the diver's acceleration is balanced against the resistance provided by the atmosphere.
