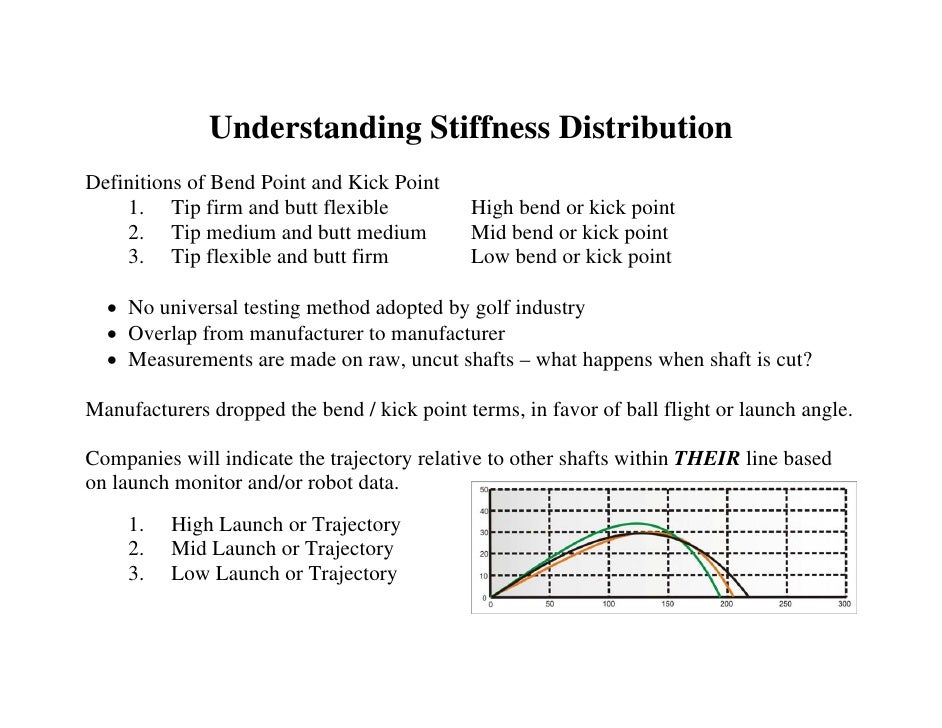
What Is Torque in a Golf Shaft?
- Definition. Torque is defined as "a force that produces or tends to produce rotation or torsion." If you think of a golf shaft as an axis, the heel of the ...
- Amount. A low-torque shaft may allow only 2 degrees (or less) of twist, while a high-torque shaft might go all the way to 6 degrees.
- Materials. ...
- The Right Amount. ...
What is the importance of torque in a golf shaft?
What Is Good Torque for a Golf Club Shaft?
- Types. A steel shaft will have less torque simply because of the material it is made of. ...
- Results. When you have less torque in your club shaft, it is said that you will have a straighter shot and a stiffer feel.
- Less Torque. When you strike the ball, you want your club head to be as square to your target as possible. ...
- More Torque. ...
- Expert Insight. ...
What does high torque mean in a golf shaft?
The torque is how much a golf club will resist bending during the swing. A golf shaft with a higher toque means that the shaft is going to twist more, and a golf shaft with a low torque will twist much less. Generally speaking, golfers with faster swing speeds are going to want lower torque golf shafts.
What is the torque rating on a golf shaft?
Still, the torque range that applies to most golfers is relatively small, between 3.5° – 5.5°. Like most clubfitting elements, there are no absolutes when it comes to matching torque to swing. The basic rules when choosing a shaft with the right torque are as follows: Golfers with high swing speeds (100+ mph) typically need lower torque shafts. Too much torque will produce excessive twisting of the clubface and wildly off-line shots.
What does torque mean in a shaft?
Torque is really pretty simple: it’s the shaft’s resistance to twisting. Torque is measured in degrees (meaning: how many degrees will the shaft twist under a certain amount of force), and you’ll typically see measurements as low as 2° and as high as 5°, 6°, or 7°.

What does the torque mean in a driver shaft?
a twisting forceTorque is defined as “a twisting force that tends to cause rotation.” In the case of a golf shaft, it's the amount of twisting (or lack thereof) that occurs during the swing.
Do I need a low torque shaft?
1) Players who tend to hook the ball will benefit from a lower torque shaft. Players who tend to slice the ball will benefit from a higher torque shaft. 2) Players who swing faster need lower torque.
What is the torque on steel golf shaft?
A steel shaft will have less torque simply because of the material it is made of. A degree of 3 to 4 is normal for a steel shaft. Graphite shafts can have a lot more torque. Since graphite is not a solid piece of material, the torque can be much higher; to degrees of 7 or 8.
How is torque measured on a golf shaft?
1:124:17How Is Golf Shaft Torque Measured? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTo measure torque I simply place my weight. And you'll see the change in the. And the torque valueMoreTo measure torque I simply place my weight. And you'll see the change in the. And the torque value and here it's two point six degrees.
What is considered low torque golf shaft?
Amount. A low-torque shaft may allow only 2 degrees (or less) of twist, while a high-torque shaft might go all the way to 6 degrees. That might not sound like a lot, but it certainly can affect your accuracy.
What is the difference between high torque and low torque?
As previously mentioned, torque tells you how an engine feels when you accelerate. Cars with high torque engines tend to accelerate slower off the mark but quicker from low revs in a high gear. Conversely, cars with low torque engines tend to accelerate quicker off the mark but slower from low revs in a high gear.
Does torque matter in golf shaft?
A high-torque shaft will twist more than a low-torque shaft. Put another way, some shafts resist twisting better than others. A shaft with a lower torque rating means the shaft better resists twisting; a shaft with a higher torque rating means the shaft is more prone to twisting (all other things being equal).
How does golf shaft torque affect ball flight?
If we think about torque affecting how the club head is delivered to the ball at impact, you can imagine that it would affect ball flight. One study in 2017, showed that shafts with a higher torque caused a more open club face at impact which led to a slightly higher launch that tended to go right.
What weight driver shaft should I use?
The shafts in the drivers of most golfers are probably in the 60 gram bracket. These shafts are light enough to help with speed yet heavy enough to give that feeling of more stability during the swing. This shaft weight will be beneficial to most golfers out there.
What does high torque mean?
At the same time, the torque should be applied over the largest possible engine speed range. In terms of driving experience, high torque means the shortest possible delay between the driver pressing the gas pedal and the engine responding.
What do numbers on golf shaft mean?
These numbers are the weight of the shaft in grams. Shaft weights typically range between 50 grams and 85 grams with the 50-60 numbers being pretty common as seen in the example shafts above.
What is torque in golf?
Warren Little / Getty Images. "Torque" is a property of golf shafts that describes how much the shaft is prone to twisting during the golf swing. All shafts, steel and graphite, exhibit torque, which is measured in degrees. A high-torque shaft will twist more than a low-torque shaft. Put another way, some shafts resist twisting better than others.
What does it mean when a shaft is high torque?
A high-torque shaft will twist more than a low-torque shaft. Put another way, some shafts resist twisting better than others. A shaft with a lower torque rating means the shaft better resists twisting; a shaft with a higher torque rating means the shaft is more prone to twisting (all other things being equal). ...
How Does Torque in Steel Shafts Compare to That in Graphite Shafts?
In steel shafts, because the type of steel material is the same throughout the entire shaft, the torque exists in a very narrow range of degrees, one that is much more narrow than in graphite shafts.
What torque is needed for a graphite shaft?
So for most golfers, as long the torque of a graphite shaft is between 3.5 and 5.5 degrees - which is the case for the vast majority of graphite shafts today - the golfer will be OK and torque will never be a factor to worry about in the shaft fitting.
How much torque does graphite have?
This allows the torque in graphite shafts to range from as high as 7 or 8 degrees to as low as 1 degree, while in steel this range is only from a little more than 2 degrees to a little under 4 degrees.
What happens if you use too high a torque rating?
a strong golfer who uses shafts with too high a torque rating might produce shots that leak to the fade side;
What is twisting in golf?
A golfer's swing, and the clubhead attached to the end of the shaft, exert forces on the shaft that lead to twisting. This twisting is simply a part of the swing.
Which player will benefit from a lower torque shaft?
1) Players who tend to hook the ball will benefit from a lower torque shaft. Players who tend to slice the ball will benefit from a higher torque shaft.
What is torque in a car?
Torque is really pretty simple: it’s the shaft’s resistance to twisting. Torque is measured in degrees (meaning: how many degrees will the shaft twist under a certain amount of force), and you’ll typically see measurements as low as 2° and as high as 5°, 6°, or 7°.
Why should you care about torque?
You should care because torque is a major component in how a shaft feels, much more than flex . You could have an XX-stiff shaft with high torque, and it might feel “smooth” or even “whippy.”. Alternately, you could have a senior flex shaft with low torque that can feel “boardy.”.
How many shots does each golfer hit with each shaft?
Each golfer hit 10 shots with each shaft and the results were measured by our FlightScope X2 launch monitor. All testing was done at the range at The Bridges of Poplar Creek Country Club.
Does Tester 3 like low torque shafts?
Tester 3 hates boardy feeling shafts, so, despite the fact that his most-hated miss is a hook, he does not like low torque shafts. On the other hand, Tester 1 doesn’t like loose feeling shafts despite the fact that he needs all the help he can get to square the club face. Historically, he has found better success with lower torque shafts because he feels like he can release the club more aggressively.
Does torque affect where the ball ends up?
Torque also has a major impact on where the ball ends up. All other things being equal, a shaft with higher torque will lead to a club face that is pointed further left (for a RH golfer) at impact…but we know “all other things” are rarely equal when you add in the human element.
Is torque a rule?
Torque matters, and, like flex and weight , there are no easy rules to follow. You need to try a variety of things and be fit into the shaft that will work best for you.
What is torque in golf?
Torque is defined as "a force that produces or tends to produce rotation or torsion." If you think of a golf shaft as an axis, the heel of the head is centered on that axis, but the toe – as well as most of the clubhead's weight – is off-center. When you swing the club, the head twists around the shaft. The toe gets "left behind" as you start your downswing, then it "catches up" and returns to its normal position at impact. The shaft resists that twisting motion, allowing only a certain amount. The twisting that is allowed, measured in degrees, is the shaft's torque.
Why do golfers use low torque shafts?
Power players such as PGA Tour golfer Dustin Johnson generally use low-torque shafts to better help them control the ball. Golf shafts have many technical specifications that you, as an average golfer, likely never consider. You are indirectly aware of them because they affect how your clubs feel when you swing them.
Why are you aware of the specs on your golf clubs?
You are indirectly aware of them because they affect how your clubs feel when you swing them. But those specs affect how your club performs, and club fitters take them into account when they fit you for new clubs. Torque is one of those "invisible" specs, and it has a bigger effect on club performance than you might expect.
How much twist does a high torque shaft have?
A low-torque shaft may allow only 2 degrees (or less) of twist, while a high-torque shaft might go all the way to 6 degrees. That might not sound like a lot, but it certainly can affect your accuracy.
What happens when you swing a golf club?
When you swing the club, the head twists around the shaft. The toe gets "left behind" as you start your downswing, then it "catches up" and returns to its normal position at impact. The shaft resists that twisting motion, allowing only a certain amount.
Does torque matter in golf shafts?
The material used to make your shaft matters. While torque always has been a factor in shaft performance, the inherent stability of steel shafts made torque relatively unimportant to everyday golfers.
Can graphite shafts be duplicated?
With the introduction of graphite shafts, however, manufacturers now can tailor shafts to behave anyway they want; they can duplicate the performance of any material from classic hickory to high-tech steel. But this comes at a price; the less torque you want, the more you have to pay for it.
What is torque in golf?
Torque is the simply the amount a golf shaft (shown in blue) twists when subjected to a known amount of force (usually one foot-pound of force is applied) and the torque value is always expressed in degrees. It is a term commonly associated with composite or graphite shafts, but steel shafts have a certain degree of torque too.
How much torque does a 46" shaft have?
For the sake of example, this 46” raw shaft (with a 43” beam length) happens to measure a torque of 6.0º using 1 foot-pound of force. By most standards, this torque rating may seem high.
Why are shafts less accurate?
One of the reasons shafts with higher torque values are considered less accurate can be attributed to the cost. Often times the higher torque wood shafts (above 6°) will be less than $9 retail and may not be 100% graphite, but have a certain percentage of fiberglass mixed in. One clue is to look at the shaft weight.
What is a low cost graphite shaft?
Low cost graphite shaft are construct ed with low modulus (lower strength) materials. Often times these shafts will exhibit both high torque and a softer tip section. In the hands of a stronger player, this combination would be less accurate than a lower torque model.
What happens if you use less material on a shaft?
If less material is used (due to the lighter weight), there is less material available to control torque or resist twisting.
Does steel have torque?
It is a term commonly associated with composite or graphite shafts, but steel shafts have a certain degree of torque too. However the amount cannot be independently changed from the frequency (or stiffness) of the shaft like a composite design, thus torque of steel shafts is generally not listed by the manufacturer.
Is there a standard for golf shafts?
I like to say “the only standard in the golf industry is there are no standards.”. Each manufacturer has an internal method for measuring torque that will vary from one to the next. However, each shaft by the manufacturer will be measured using the exact same clamping dimensions and force for all their shafts.
Why is shaft torque important?
Shaft torque becomes increasingly important the faster you swing. Torque is the measure of how much the shaft twists during the golf swing. It may be hard to imagine this even happening, but shafts are made with that particular fact in mind. They are even made to resist it more or less, depending on your swing and what kind ...
What happens when you have less torque in your golf club shaft?
When you have more torque in your club shaft it is said that your shots can be less accurate but go further and have a nice soft feel.
Why does my golf club go faster?
This also means you can hit the ball a little further, because at the time the club strikes the ball the torque can cause the club head to go faster.
Why does a steel shaft have less torque?
A steel shaft will have less torque simply because of the material it is made of. A degree of 3 to 4 is normal for a steel shaft. Graphite shafts can have a lot more torque. Since graphite is not a solid piece of material, the torque can be much higher; to degrees of 7 or 8.
Does Tiger Woods know how much torque he needs?
Certainly Tiger Woods knows exactly how much torque he needs for every club in his bag , but for a beginner it won't matter much. Torque should be one of the last things you look at when trying to improve your game. Golfweeks' Adam Woodard breaks down the results from the match.
Why use a lower torque shaft?
This allows them to benefit from a better energy transfer (i.e. more shaft “kick”) while taking advantage of the added stability a lower torque provides .
Why does a higher torque shaft cause a club to twist?
And because this shaft has a high torque, it won’t “snap back to square” as quickly as necessary, which is why higher-torque shafts tend to create a more rightward dispersion for a right-handed golfer.
WHAT IS TORQUE?
Shaft torque is measured by a device that records the amount a shaft will twist under a certain amount of force, and it’s recorded in degrees. A shaft with 3 degrees of torque will twist less than a shaft with 5 degrees of torque, and so on.
How does torque affect dispersion?
While it’s true that low-torque shafts are more resistant to twisting, it’s this same resistance to twisting that actually causes a shaft to “snap back to square” more easily than higher-torque shafts at impact and thus produce a tendency to move dispersion to the left.
What shafts help with left and right dispersion?
A lower-torque shaft will help a golfer create a more leftward dispersion. A higher-torque shaft will help a golfer create a more rightward dispersion. These guidelines seem to fly in the face of conventional wisdom about shaft torque, which has long stated that lower-torque shafts help golfers avoid a snap hook due to their greater resistance ...
What is a red range shaft?
Their low-torque design gives golfers the opportunity to maximize swing speed and ball speed with a lighter, softer shaft than they’re often used to playing while maximizing club face control through a lower torque.
Why is a golf shaft stiffer?
The reason for this relationship is that a golf shaft is both bending and twisting at the same time during a golf swing, which means that stiffer shafts will benefit from a lower torque. It wouldn’t make sense to make a very stiff shaft with a very high torque.
What does low torque mean on a golf shaft?
The lower the torque number — it’s measured in degrees — the more resistant the shaft is to unwanted twisting. For someone like Tiger Woods or Rory McIlroy, who generate top-end speed with the driver, having an uber-stable shaft with low torque ensures they can go after the ball and not have to worry about speed affecting launch angle, spin rate and dispersion.
Why are low torque shafts so expensive?
“As you go up in grade of material, which is actually going up in stiffness and strength of the material, you essentially double the cost of the material for every step you take up ,” said designer John Oldenburg.
What shaft is Tiger Woods?
Tiger Woods' Mitsubishi Diamana D+ Plus shaft is an example of a low torque product.
What materials are used to stabilize a golf swing?
Torque can be controlled a number of different ways, but the most common is utilizing exotic materials — including Kevlar, Carbon, Boron and Zylon — to stabilize the shaft. Accomplishing this makes the profile more resistant to unwanted twisting during the swing, especially at impact. In other words: improved consistency.
Does every shaft have torque?
Not every shaft has the torque number emblazoned on the shaft, but if you happen to play a Project X HZRDUS or Aldila Rogue — these are just a few examples — you might notice a number with a decimal point that looks somewhat out of place. It’s too small to be the shaft weight or flex (in the case of Project X products), which leaves us with one other option: shaft torque.