How much oil flows through the Strait of Hormuz each year?
Flows through the Strait of Hormuz in 2018 made up about one-third of total global seaborne traded oil. More than one-quarter of global liquefied natural gas trade also transited the Strait of Hormuz in 2018. There are limited options to bypass the Strait of Hormuz.
How much oil does the Persian Gulf produce a day?
Oil production capacity of 25.4 million barrels per day (33 percent of the world total) at the end of 2006 The Persian Gulf exports approximately 18.2 million barrels of oil per day; approximately 17 million barrels per day transit through the Strait of Hormuz in tankers.
What will happen if the Strait of Hormuz is blocked?
The blockage of the Strait of Hormuz, even temporarily, could lead to substantial increases in total energy costs.
How much oil passes through the Gulf of Mexico each day?
WHY IT MATTERS? * The U.S. Energy Information Administration estimates a record 18.5 million barrels per day of sea-borne oil passed through it in 2016, a 9 percent increase on flows in 2015 which accounted for 30 pct of all sea-borne traded crude oil and other liquids during the year.

How much oil does the Strait of Hormuz take?
21 million barrelsThe narrow strait is the most important chokepoint for the world's oil supply. Some 21 million barrels — or $1.2 billion worth of oil — pass through the strait every day.
How much oil does the Gulf have?
This publication presents the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management's (BOEM) estimates of oil and gas reserves in the Gulf of Mexico Outer Continental Shelf. As of December 31, 2018, it is estimated that the Original Reserves are 24.86 billion barrels of oil and 195.5 trillion cubic feet of gas from 1,319 fields.
Who has more oil Saudi or Iran?
This is a list of countries by proven oil reserves....SourceUS EIAIran157.8Iraq145Russia80.0Saudi Arabia268.33 more columns
Who has the most oil in the Middle East?
Saudi ArabiaSaudi Arabia Saudi Arabia is the world's largest oil producer and accounts for roughly 15% of global output. Iraq has increased production since the end of the Iraq War and is now the second-largest producer in the Middle East.
Why was the Strait of Hormuz important?
The Strait of Hormuz is an area of potential violent conflict; it was an important aspect of the Iran-Iraq war in the 1980s because the flow of oil through the region places international interests on the gateway.
When will oil flow through the Strait of Hormuz?
The Economic Times. (2021). Oil flows through the Strait of Hormuz between 2014 and 2020 (in million barrels per day). Statista. Statista Inc.. Accessed: November 28, 2021. https://www.statista.com/statistics/277157/key-figures-for-the-strait-of-hormuz/
How much oil does the Persian Gulf export?
The Persian Gulf Region and Global Energy (as a % of global) The Persian Gulf exports approximately 18.2 million barrels of oil per day; approximately 17 million barrels per day transit through the Strait of Hormuz in tankers.
How much natural gas is transported through the Strait of Hormuz?
Additionally, over 3.5 billion cubic feet of natural gas, approximately 18 percent of world shipments, travel through the Strait via LNG tankers . [ii] There are few alternate routes for exporting Persian Gulf oil and gas, making the Strait of Hormuz an important chokepoint.
Where is the Persian Gulf oil shipped?
Persian Gulf oil is shipped east to Asia, primarily to Japan, China, and India, and west to Western Europe and the United States.
What is the EIA's World Oil Transit Chokepoints analysis brief?
EIA's World Oil Transit Chokepoints analysis brief contains additional information on Hormuz and the other chokepoints, and the Middle East & North Africa overview contains additional information about countries in the region.
How many barrels of oil are consumed in 2011?
In 2011, total world crude oil and liquefied fuels consumption amounted to approximately 88 million barrels per day (bbl/d), and more than one-half was moved by tankers on fixed maritime routes. Chokepoints are narrow channels along widely used global sea routes, some so narrow that restrictions are placed on the size of the vessel that can navigate through them. The map shows chokepoints that are critical areas for global energy security because of the high volume of oil that moves through waterways.
Why are chokepoints important?
The map shows chokepoints that are critical areas for global energy security because of the high volume of oil that moves through waterways.
How much oil does the Kirkuk-Ceyhan pipeline transport?
1Although the Kirkuk-Ceyhan Pipeline has a nominal nameplate capacity of 1.6 million bbl/d, its effective capacity is 0.4 million bbl/d because it cannot transport additional volumes of oil until the Strategic Pipeline to which it links can be repaired to bring in additional volumes of oil from the south of Iraq.
What is unused capacity?
2"Unused Capacity" is defined as pipeline capacity that is not currently utilized and can be readily available.
Which countries have oil pipelines to bypass Hormuz?
Among the major oil exporters that ship oil through the Persian Gulf, only Iraq, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) presently have pipelines to bypass Hormuz, and only the latter two countries currently have unutilized pipeline capacity on these pipelines.
Where is the Abu Dhabi oil pipeline?
The UAE recently opened a 1.5 million bbl/d Abu Dhabi Crude Oil Pipeline, which runs from Habshan, a collection point for Abu Dhabi's onshore oil fields, to the port of Fujairah on the Gulf of Oman , allowing crude oil shipments to circumvent Hormuz.
What was the Carter doctrine?
The Carter Doctrine, as it came to be known, was implemented with the creation of Central Command (CENTCOM), to keep tab of any dangers. In 87-88, when Iran threatened oil tankers of Kuwait and Saudi Arabia, the tankers were escorted by U.S. war ships. Later, the same CENTCOM would invade Iraq during the Gulf wars.
What aircraft carrier entered the Persian Gulf?
In anticipation of such belligerent moves, the aircraft carrier USS Abraham Lincoln has entered the Persian Gulf escorted by six British and French naval forces. It's a cat and mouse game: Should Iran do anything, the 100,000-tonne aircraft carrier wouldn't be a mute spectator.
What would happen if Iran blocked the waterway?
If blocked, it would be through a series of means - mines, missiles, small boats armed with suicide squads, attack through sub-marines (Iran has miniature submarines which could be launched in shallow waters).
What is the new sanctions on Iran?
This law, apart from targeting the revenue from oil imports, also targets financial institutions from other countries that conduct transaction with Iran's central bank.
Why is Iran a winner of the Arab Spring?
Further, Iran is the winner of the Arab spring as it has successfully exported its government structure into other Arab nations.
How far can Iran cruise missiles reach?
However, some unintentional accidents can change the dynamics, such is the pressure. If the conflict goes all out, Iran has cruise missiles with a range of 11,500km, capable of reaching all of Europe as well as Eastern US including New York.
What countries does Hormuz control?
Hormuz controls access to oil from Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, the UAE and Iran. 20% of the world'd oil would stagnate if Iran closed the strait of Hormuz.
US-Iran tensions
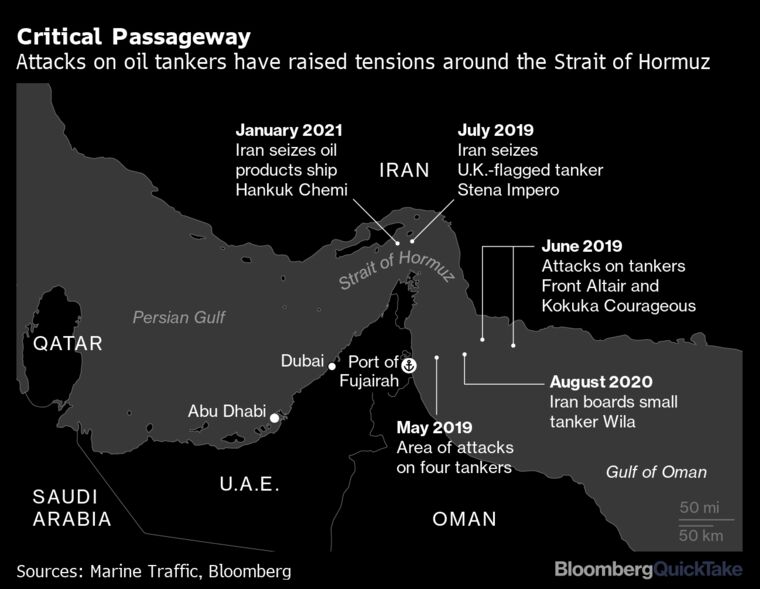
The Gulf region has been shaken by a period of heightened instability in recent months, threatening the flow of oil through the Strait. Six oil tankers and a U.S. spy drone have been attacked since May in, or near, the waterway amid intensifying tensions between the U.S. and Iran.
Which countries depend on oil shipped via the Strait?
The EIA estimated that 76% of the crude oil and condensate that moved through the chokepoint went to Asian markets in 2018.
What is the busiest passageway for oil tankers?
The Strait of Hormuz is the busiest passageway for oil tankers in the world, with over 17 million barrels (or 20% of the total world supply) moving through the narrow stretch of water each day.
How much money has the US spent protecting the Straits of Hormuz?
The U.S. has Spent $8 Trillion Protecting the Straits of Hormuz. A group of nine student journalists from the Medill National Security Journalism Initiative have created a website as part of a project to report on the US energy security situation.
How much money did the US spend on oil in the Persian Gulf?
Roger Stern, a professor at the University of Tulsa National Energy Policy Institute, wrote a study in 2010 in which he estimated that the US had spent $8 trillion on protecting oil cargoes in the Persian Gulf since 1976, when its military presence in the region was boosted following the first Arab oil embargo.
Why did the US go to the Gulf?
Stern explained the true meaning behind the US’s reasons for heading to the Gulf en masse in an interview: “The fear grew out of a belief not just in a global peak oil, but a strong CIA conviction, that was shared by the National Security Council, that the Soviets were running out of oil, that their production was going to tank in just a few years and the Soviets had no choice but to march to the Persian gulf to get oil, so that was the rationale for the idea that a force was needed.”
Where did James Burgess study?
James Burgess studied Business Management at the University of Nottingham. He has worked in property development, chartered surveying, marketing, law, and accounts. He has also…
What is the name of the chokepoint between the Arabian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman?
The Strait of Hormuz is the world’s single most important oil passageway, forming a chokepoint between the Arabian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. The 39km strait is the only route to the open ocean for over one-sixth of global oil production and one-third of the world’s liquified natural gas (LNG).
What is the key waterway out of the Gulf of Oman?
Explaining the economic and geopolitical significance of the key waterway out of the Gulf. The Strait of Hormuz is the world’s single most important oil passageway, forming a chokepoint between the Arabian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman.
How much oil passes through the strait?
How much oil and gas passes through? Around one-sixth of the world’s oil moves through the strait – 17.2 million barrels per day. This includes most of the oil from Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) members Saudi Arabia, Iran, the UAE and Kuwait.
Why are the UAE and Saudi Arabia building more oil pipelines?
For this reason, the UAE and Saudi Arabia have proposed building more oil pipelines to avoid the problematic waterway.
What happened in the 1980s?
During the Iran-Iraq War in the 1980s, the two countries routinely menaced each other’s oil shipments. In 1988, US warship Vincennes shot down an Iranian passenger plane, killing 290 people in what Washington said was an accident. In 2010, a Japanese oil tanker was attacked by a group linked to al-Qaeda.
Where were the Saudi tankers attacked?
In May 2019, four vessels – including two Saudi oil tankers – were attacked near Fujairah just beyond the strait. While the June 13 attacks on two oil tankers in the Gulf of Oman raised fears about the global oil supply and new questions about the security of shipments through the Strait of Hormuz.
Where is the Strait of Hormuz?
Where exactly is the Strait of Hormuz? It lies between Oman and Iran, linking the sea passage from the countries on the Gulf (Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates) with the Arabian Sea and beyond.