Full Answer
What is the shape of a myosin molecule?
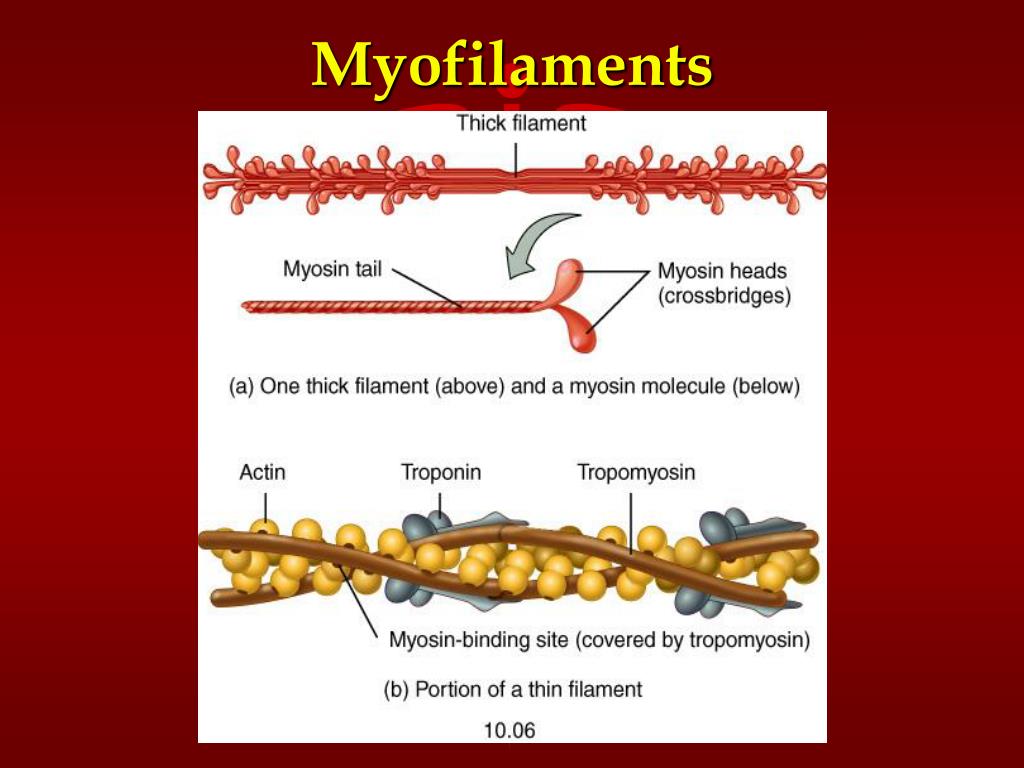
A myosin molecule is shaped like a golf club, with a tail formed of two intertwined chains and a double globular head projecting from it at an angle. Half of the myosin heads angle to the left and half of them angle to the right, creating an area in the middle of the filament known as the bare zone.
What is the shape of actin myosin tropomyosin ATP?
actin myosin tropomyosin ATP Ca^2+ ATP *ATP supplies the energy necessary for muscle contraction. (section 13.02) Each actin molecule is shaped like a golf club, with a straight portion ending in a globular head. True False false *Each myosin molecule is shaped like a golf club. (section 13.02)
What is the shape of the actin molecule?
(section 13.02) Each actin molecule is shaped like a golf club, with a straight portion ending in a globular head. True False false *Each myosin molecule is shaped like a golf club.
What is the structure of a myofilament?
Structure. There are three different types of myofilaments: thick, thin, and elastic filaments. Thick filaments consist primarily of the protein myosin. Each thick filament is approximately 15 nm in diameter, and each is made of several hundred molecules of myosin. A myosin molecule is shaped like a golf club,...

What structure in a muscle is shaped like a golf club?
tail Myosin is a protein that is shaped as a golf club with the tail forming the shaft of the club.
What is the shape of the myosin head?
pear-shapedWhen the myosin heads are observed on a whole molecule, their length is ≈19 nm and they are pear-shaped.
Are cross-bridges myosin heads?
As soon as the actin-binding sites are uncovered, the high-energy myosin head bridges the gap, forming a cross-bridge. Once myosin binds to the actin, the Pi is released, and the myosin undergoes a conformational change to a lower energy state.
What is formed by the myosin head?
The globular heads of myosin bind actin, forming cross-bridges between the thick and thin filaments.
What is the structure of myosin?
Myosin molecules comprise two heavy chains and four light chains. The C-terminal parts of the myosin heavy chains (MHC) twist together to form the 1500 Å-long coiled-coil α-helical rod-shaped tail domain (Figure 3a). The N-terminal parts of the heavy chains form the two myosin heads (Figure 4a).
What is globular head?
Globular head of myosin contains an ATPase enzyme that along with CO2+ and mg2+ ions catalyses the breakdown of ATP during muscle contraction. If also has binding site for ATP and active sites for actin.
What is the myosin actin cross-bridge?
0:032:49Muscle Contraction - Cross Bridge Cycle, Animation. - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe troponin units on the actin.MoreThe troponin units on the actin.
What is myofilament with a knob like head?
Myosin. Myofilament with a knob-like head that attaches in cross-bridging. Actin. Myofilament stiffened and stabilized by tropomyosin.
What do myosin cross bridges do?
Actin and myosin crossbridge cycling: Actin and myosin are filamentous proteins which interlock and overlap in a way to produce length change and tension development in skeletal muscle.
What causes the myosin heads to change shape?
As soon as actin's binding sites are exposed, the nearby myosin heads bind to the actin. This binding causes the myosin to change shape dramatically, bending at a hinge where the head attaches to the filament. As a result, the myosin pulls on the actin, causing the two filaments to slide past one another.
What is the tertiary structure of myosin?
0:338:21032-Myosin Structure & Function - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo there are two polypeptide chains each chain contains a globular head region. There's a longMoreSo there are two polypeptide chains each chain contains a globular head region. There's a long straight neck region and an alpha helical tail as these associate to form dimers.
Why does myosin have two heads?
These data suggest that muscle myosins require both heads to generate maximal force and motion. Muscle shortening is driven by a cyclical interaction between the contractile proteins myosin and actin. During this cycle the dimeric molecular motor, myosin, transduces chemical energy into mechanical work.
Does myosin have two globular heads?
Each molecule of myosin has a rodlike tail and two globular heads (Figure 2-7, A). A typical thick filament contains approximately 200 myosin molecules. These molecules are oriented so that the tails form the central rodlike structure of the filament (Figure 2-7, B).
Why does myosin have two heads?
These data suggest that muscle myosins require both heads to generate maximal force and motion. Muscle shortening is driven by a cyclical interaction between the contractile proteins myosin and actin. During this cycle the dimeric molecular motor, myosin, transduces chemical energy into mechanical work.
What are the three heads of myosin filament?
Myosin is the major component of the thick filaments and most myosin molecules are composed of a head, neck, and tail domain; the myosin head binds to thin filamentous actin, and uses ATP hydrolysis to generate force and "walk" along the thin filament.
How does the myosin head resume its normal position?
The myosin head resumes its normal position using energy from the hydrolysis of ATP.
How many muscle fibers can a motor neuron stimulate?
One motor neuron activates one muscle fiber. *One motor neuron can stimulate from a few to several muscle fibers of a muscle because each axon has several branches. *All the muscle fibers in a motor unit are stimulated at once. They all either contract or do not contract. Why is the innervation ratio in the ocular muscles one motor axon per 23 ...
What is a tic in the foot?
A tic is a strong, and very painful spasm, especially of the leg and foot. A tic is caused by stretching or tearing of a muscle, while a spasm is just an involuntary contraction. A tic is caused by the inflammation of a tendon, while a spasm is just an involuntary contraction.
Which muscle has the fewer fibers per motor axon?
The innervation ratio has to do with the overall size of the muscle--the bigger the muscle, the fewer the muscle fibers per motor axon. The gastrocnemius muscle contracts much harder than the ocular muscles do. There are fewer muscle fibers in the gastrocnemius muscle than in the ocular muscles. The ocular muscles require finer control ...
What is the term for the inflammation of the bursa?
Bursitis is the inflammation of the bursa. Muscular dystrophy is a progressive degeneration of muscles. Fibromyalgia is a temporary condition of achy muscles, usually due to overuse. *Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition whose symptoms include achy pain, tenderness, and stiffness of muscles.
What happens when myosin-actin crosses bridges?
The myosin-actin cross-bridges are broken and the sarcomere shortens. The neurotransmitter is diffusing across the synaptic cleft causing an electrical signal in the muscle cell. The neurotransmitter is diffusing across the synaptic cleft causing an electrical signal in the muscle cell.
Which muscle fibers are fewer than the ocular muscle fibers?
There are fewer muscle fibers in the gastrocnemius muscle than in the ocular muscles. The ocular muscles require finer control than moving the legs. *The ocular muscles require much finer control than moving the legs. (section 13.03)