Who were the Native Americans of the Gulf Coast?
Native Americans lived in the Gulf Coast region of Texas for thousands of years. They lived together in small groups of about 25-50 people. Each group had their own name and clothing styles and spoke slightly different languages. Today, we know that most of these Native Americans belonged to one of two cultures: the Atakapa or the Karankawa.
Where do the indigenous people live in Mexico?
The indigenous population is distributed throughout the territory of Mexico, but is especially concentrated in the Sierra Madre del Sur, the Yucatan Peninsula and in the most remote and difficult-to-access areas, such as the Sierra Madre Oriental, the Sierra Madre Occidental and neighboring areas.
Where did Native Americans live in Texas?
Native Americans lived in the Gulf Coast region of Texas for thousands of years. They lived together in small groups of about 25-50 people. Each group had their own name and clothing styles and spoke slightly different languages.
What kind of Indians live in Baja California?
Northern Mexican Indian. The remnants of the Baja California Indians—the Tiipay (Tipai; of the Diegueño ), Paipai (Akwa’ala), and Kiliwa—live in ranch clusters and other tiny settlements in the mountains near the U.S. border. Speaking Yuman languages, they are little different today from their relatives in U.S. California.

Which Native American group traveled across the Gulf of Mexico?
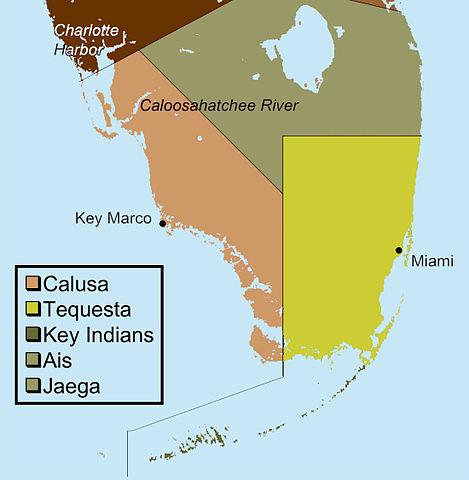
The Calusa Indians were originally called the "Calos" which means "Fierce People." They were descendants of Paleo-Indians who inhabited Southwest Florida approximately 12,000 years ago. During the Calusa's reign the Florida coastline extended roughly 60 miles further into the Gulf of Mexico.
What two Native American groups were nomads along the Gulf?
By the mid-1800s, the Karankawa had died out from European diseases and from many battles with European groups. The Karankawa (kah ran KAH wah) lived south of the Caddo, along the coast of the Gulf of Mexico. They were nomads.
What small Native American tribe originally lived on the Gulf coast and whose name means first people?
The Olmec were the first major civilization in Mexico. They lived in the tropical lowlands on the Gulf of Mexico in the present-day Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco. The name Olmec is a Nahuatl—the Aztec language—word; it means the rubber people.
Which tribe lived in the Gulf coast by Padre Island?
More than one tribe of Coahuiltecans inhabited the region of Padre Island, including the Malaquites who lived in circular huts with wooden frames that they covered with animal skins.
What tribes were in the Gulf culture?
Today, we know that most of these Native Americans belonged to one of two cultures: the Atakapa or the Karankawa. The Atakapas lived in the northern part of the coast. The Karankawas lived on the southern part of the coast. Both Atakapas and Karankawas hunted ducks and geese and ate turtles.
What is the Comanche tribe known for?
The Comanche were known for being strong warriors and having the finest horses. Today, they celebrate their heritage with an annual powwow, or dancing festival, in July.
What is the oldest Native American tribe?
The Hopi IndiansThe Hopi Indians are the oldest Native American tribe in the World.
Where did the Choctaw tribe live?
southeastern MississippiChoctaw, North American Indian tribe of Muskogean linguistic stock that traditionally lived in what is now southeastern Mississippi.
Who were the 13 original tribes of Long Island and where did they live?
When the Island was first settled by the whites it was inhabited by 13 tribes or groups of Indians. The Canarsee, Rockaway, Merrick, Marsapeague, Secatogue, and Unkechaug lived on the South Shore. On the north were the Matinecock, Nesaquake, Setalcott, and Corchaug.
What tribe lived in the western Gulf coastal plain?
Many tribes settled along this slow arch of coastline, inhabiting land that today stretches from Florida to Texas; a selection of these groups, moving east to west, included the Calusa, the Apalachee, the Chitimacha, and the Karankawa.
How did the Karankawa look like?
Karankawas were known for their distinctive physical appearance. In the sixteenth and seventeenth century the men were described as tall and muscular, and during the summer wore deerskin breechcloths or nothing at all. Come winter, these Indians donned buffalo and deer robes for warmth.
Do the Karankawa still exist?
The Karankawa went extinct as a distinct tribe in the late 19th century.
What is the northern Mexican Indian?
Northern Mexican Indian, member of any of the aboriginal peoples inhabiting northern Mexico. The generally accepted ethnographic definition of northern Mexico includes that portion of the country roughly north of a convex line extending from the Río Grande de Santiago on the Pacific coast to the Río Soto la Marina on the Gulf of Mexico.
What are the dominant people of Mexico?
Many groups faded away—gradually losing their languages and identities in the emerging mestizo (mixed-race European and Indian) population, the predominant people of present-day Mexico. Only the Huichol, Seri, and Tarahumara retained much of their pre-contact cultures.
Where are Cora and Huichol from?
Huichol and Cora, neighbouring Middle American Indian peoples living in the states of Jalisco and Nayarit in western Mexico. Numbering together about 40,000 in the late 20th century, they inhabit a mountainous region that is cool and dry. The Huichol and Cora languages are about as closely related….
Which region is more arid and less favourable for human habitation than central Mexico?
This southern boundary coincides in a general way with the northern margins of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica. Northern Mexico is more arid and less favourable for human habitation than central Mexico, and its native Indian peoples have always been fewer in numbers and far simpler in culture than those of Mesoamerica.
Where are Cocopa found?
A small number of Cocopa in the Colorado River delta in like manner represent a southward extension of Colorado River Yumans from the U.S. Southwest. The remaining group is the Seri, who are found along the desert coast of north-central Sonora.
Who were the first non-Indians to explore the Texas coast on land?
These survivors were the first non-Indians that we know of to explore the Texas coast on land. Eventually, they left the Karankawa and traveled across Texas and Mexico to find other Spaniards. Cabeza de Vaca was one of the survivors, and he wrote a famous book about their life in Texas.
Why did the Spanish build missions and forts in the Gulf Coast Region?
When they finally found it, they were very sad for the people who had died there. After Fort St. Louis was destroyed, the Spanish built missions and forts in the Gulf Coast Region to keep the French out.
What two cultures did the Atakapas belong to?
Today, we know that most of these Native Americans belonged to one of two cultures: the Atakapa or the Karankawa. The Atakapas lived in the northern part of the coast. The Karankawas lived on the southern part of the coast.
Why did the Karankawa move away from the coast?
For instance, in the spring and summer, the Karankawa moved away from the coast to hunt deer and harvest pecans. In the fall and winter, they lived on the coast and ate oysters, fish and roots.
What is important to remember about the indigenous tribes that lived along the lower parts of the Rio Grande?
Before reading this report about the indigenous tribes that lived along the lower parts of the Rio Grande, it is important to remember that different chroniclers and authors assembled their information from disparate sources. Not all the historians are in agreement about the names and dispositions of each tribal group, and some tribal groups were known by multiple names.
Where did the Coahuiltecans live?
The Coahuiltecan tribes were made up of hundreds of autonomous bands of hunter-gatherers who ranged over the eastern part of Coahuila, northern Tamaulipas, Nuevo León and southern Texas south and west of San Antonio River and Cibolo Creek. It was the practice of the Coahuiltecans to move from one traditional campsite to another, following the seasons and herds of migrating animals.
What are the four cultures in the Tamaulipas region?
According to Saldívar, when the Spaniards arrived, they found four cultures in the area of present-day Tamaulipas. Of the four cultural groups, Saldívar described the Grupos del Norte (“Groups of the North”) who inhabited the northernmost region as nomadic groups that lived mainly in the area between the Purificación and Bravo Rivers (The Río Bravo is known as the Rio Grande to Americans today). These numerous small northern Tamaulipas tribes appeared to speak closely-related languages and shared the same basic culture.
What is Martin Salinas' role in the history of Southern Texas and Northeastern Mexico?
Martin Salinas’ Indians of the Rio Grande Delta: Their Role in the History of Southern Texas and Northeastern Mexico (1990) makes a good English language resource for people who would like to study the tribal groups along the Rio Grande. Martin Salinas describes the historical mention of each tribe over time.
Who clustered all the Coahuiltecan bands around a central, dominant band?
Ruecking clustered all the Coahuiltecan bands “around a central, dominant band.” Referred to as “band-clusters,” these groups were “bound together by (1) geographic proximity, (2) historic association, (3) cultural or linguistic affinity, and/or (4) a similarity in band names. In his thesis, Ruecking recognized eight band-clusters, suggested three more and indicated four others as possibilities.
Who wrote Los Indios of Tamaulipas?
In 1943, musicologist, teacher and historian, Gabriel Saldívar Silva, wrote Los Indios of Tamaulipas, to provide the names of many of these indigenous groups, most of which were eventually assimilated into colonial society and disappeared as distinguishable cultural entities.
When was the Rio Grande River settled?
This boundary was finalized in 1848, but a century earlier, much of the Rio Grande River area was being settled by Spanish and Mexican settlers who had come from other parts of Mexico to settle the lands that were already inhabited by many tribal groups.

Overview
Indigenous peoples of Mexico (Spanish: gente indígena de México, pueblos indígenas de México), Native Mexicans (Spanish: nativos mexicanos) or Mexican Native Americans (Spanish: pueblos originarios de México, lit. 'Original peoples of Mexico'), are those who are part of communities that trace their roots back to populations and communities that existed in what is now Mexico prior t…
Definition
In the second article of its Constitution, Mexico is defined as a "pluricultural" nation in recognition of the diverse ethnic groups that constitute it and where the indigenous peoples are the original foundation.
The number of indigenous Mexicans is judged using the political criteria found in the 2nd article of the Mexican constitution. The Mexican census does not report racial-ethnicity but only the cultur…
History
The prehispanic civilizations of what now is known as Mexico are usually divided in two regions: Mesoamerica, in reference to the cultural area where several complex civilizations developed before the arrival of the Spanish in the sixteenth century, and Aridoamerica (or simply "The North") in reference to the arid region north of the Tropic of Cancer where few civilizations developed and was mostl…
Rights
The Spanish crown had legal protections of indigenous as individuals as well as their communities, including establishing a separate General Indian Court. The mid-nineteenth century liberal reform removed those, so that there was equality of individuals before Mexican law. The creation of a national identity not linked to racial or ethnic identity was an aim of Mexican liberalism.
Development and socio-economy
Generally, indigenous Mexicans live more poorly than non-indigenous Mexicans, though social development varies between states, different indigenous ethnicities and between rural and urban areas. In all states indigenous people have higher infant mortality, in some states almost double of the non-indigenous populations.
Demographics
The number of indigenous Mexicans is judged using the political criteria found in the 2nd article of the Mexican constitution. The Mexican census does not report racial-ethnicity but only the cultural-ethnicity of indigenous communities that preserve their indigenous languages, traditions, beliefs, and cultures.
The Law of Linguistic Rights of the Indigenous Languages recognizes 62 indig…
Education
Mexico is the nation of the Americas with the highest number of living languages in the early years of the 21st century, despite this cultural wealth, there is a technological disparity in education for indigenous peoples compared to other ethnic groups living in the country.
With the creation of the SEP, the first indigenous education works for children …
Culture
The Mexican Indigenous communities are enriched on celebrations, traditional costumes, oral heritage, medicine, literature, architecture and music by gender-separated groups. It includes parades of indigenous walking bands, native food, and statewide artisanal crafts, such as Pre-Hispanic-style textiles. Each costume and dance usually has a local indigenous historical and cultural meaning.